
Active ingredients commonly used in medicated pigmentation creams in Malaysia
Medicated Pigmentation Creams in Malaysia
Hyperpigmentation skin problem is a common skin disorder affecting the face many Malaysian. It is associated with considerable psychological stigma and distress. The management of some of these pigmentation conditions, especially melasma, can be challenging. It often requires a long-term treatment plan and multiple modalities to treat it. On top of avoidance of aggravating factors such as hormonal pills and excessive sun exposure, topical skincare products and prescription-only pigment creams are the most common treatment in Malaysia. The common active ingredients in prescription-only medicated pigmentation creams include, hydroquinone, steroids, retinoids and azelaic acid. This article will discuss about these ingredients and aim to give readers some insight about them.
Active ingredients commonly found in over the counter skincare products in Malaysia are discussed in previous article.
Hydroquinone
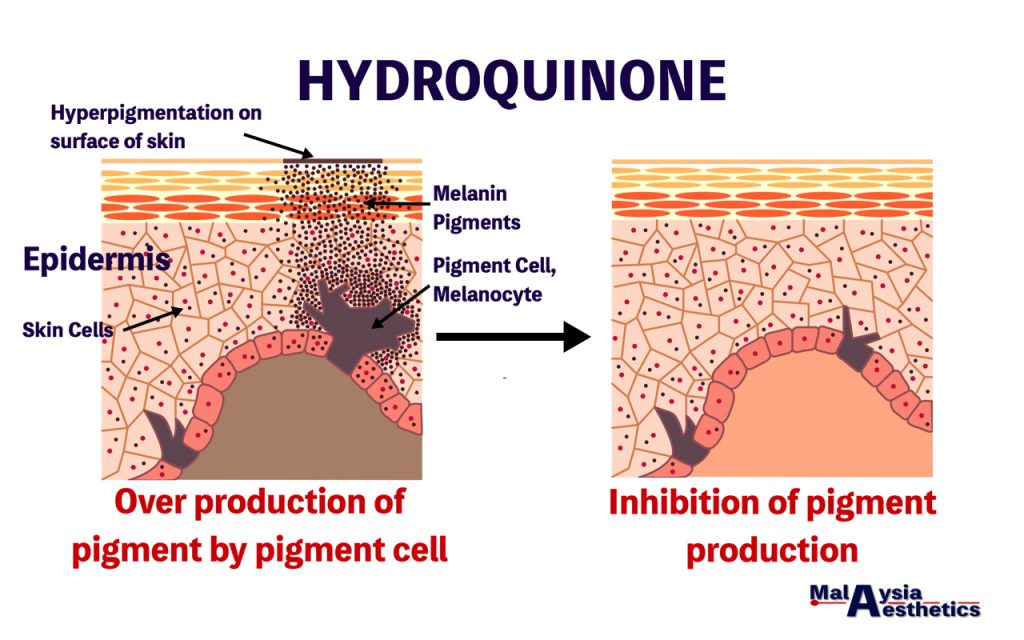
Hydroquinone (HQ), also known as dihydroxybenzene is a compound that stops the production of melanin (pigment) by the melanocyte (pigment cell). Studies have shown that HQ not only reduce the production of melanin, but could potentially causes necrosis (cell death) to the melanocyte (pigment cell).
HQ is the most frequently prescribed depigmentating agent worldwide, including Malaysia. It has remained the gold standard for the treatment of melasma. In Malaysia, HQ is listed in the first schedule poison list. Hence, HQ should only be used under close monitoring of a trained and certified dermatologist or medical aesthetic doctor.
HQ containing depigmentating creams in Malaysia typically contain 2-5% of hydroquinone. Most HQ cream is recommended for once daily use, best at night time. HQ creams typically gives good results after 5-7 weeks. Many HQ containing cream in the market combines other agents like sunscreens, topical steroids, retinoids or alpha hydroxy acids (Glycolic acids) for better clinical result. HQ has the tendency to oxidize, turning the color of the cream from white to brown. Formulation that have undergone this color change are ineffective and should be discarded.
Adverse reactions associated with usage of HQ are dependance to its dose and duration of treatment. The most common reported complication from HQ use is skin irritation. A person may feel stinging and burning sensation or the skin may become red. For those who use highly concentrated HQ creams are at risk of developing ‘confetti-like’ depigmentation (white spots). There are also reports of skin pigmentation worsen following the use of HQ creams (paradoxical postinflammatory hypermelanosis). A rare complication associated with prolonged usage of HQ cream is ochronosis, a blue-black pigmentation at the treated skin. Recovery from ochronosis is usually slow even after avoidance of the offending agents.
In Malaysia, the use of hydroquinone has been banned in cosmetic products. The use of hydroquinone should be closely monitored by trainded doctors to minimise the occurance of potential disfiguring adverse reactions.
Topical Steroids
For centuries, steroids containing creams are used extensively in dermatology practice. A well-known unwanted effect of prolonged steroid usage is depigmentation (whitening) of the treated skin. Although the exact mechanism behind its effect is not clearly understood, it is believe that steroids anti-inflammatory effect of steroids influence the production of melanin (pigment) by the melanocyte (pigment cell). Although steroid have good depigmentating property, it should not be used on its own for treatment of skin pigmentation.
In Malaysia, topical steroids are usually used in combination with different active depigmentating ingredients. One popular example of this is, Kligman’s formula. This formulation cream uses the combination of topical steroids with HQ and retinoid. Many clinical trials have shown that this combination cream delivers good results, especially in treating melasma.
Adverse effects reported with the use of topical steroids include skin irritation, acne eruptions, broken capillaries (telangiectasia), skin thining (Atrophy) and hypertrichosis (excessive hair growth). Topical steroid is also listed in the Malaysian health ministry’s (MOH) schedule 1 poison list. Hence, doctor’s prescription and monitoring is needed when using topical steroids.
Retinoids
Retinoids, such as Retin-A, or tretinoin, were first used in combination with HQ to enhance the penetration of the latter. As our understanding of retinoid increases, we now recognize their direct effect on pigment formation. Retinoids affect skin’s melanin (pigment) formation in various ways. Firstly, retinoids increase the epidermal (outermost layer of the skin) turnover, hence decreasing the contact time between the skin cells and the pigment cells. It also reduce the enzymatic activity involved in pigment production, hence reducing the overall pigment formation.
Studies have shown that the use of retinoid alone in treating hyperpigmentation skin can produce good clinical improvement. However, combining other agents like HQ and steroids can produce better clinical result. Compared to HQ, retinoids takes a longer time to act and significant clinical improvement on hyperpigmentation only bnecomes evident after about 24 weeks.
The most common side effects encountered incude redness, skin irritation and peeling. These reaction might result in post-inflammatory hyperpigmentation especially in people with dark skin type. For those who are on retinoids cream, the use of sun screens is strongly recommended.
Azelaic acid
Initially developed as a topical anti-acne agent, azelaic acid has been used to treat skin hyperpigmentation such as melasma. This is because azelaic acid inhibits tyrpsinase, an enzyme crucial in the production of melanin pigment. Azelaic acid is beneficial for those with post-inflammatory hyperpigmentation associated with acne. There are studies to suggest that azelaic acid may have similar efficacy if not better than hydroquinone, but without the side effects associated with hydroquinone. However, more studies are required before we make a definitive conclusion.
In Malaysia, azelaic acid is also listed in the Ministry of Health’s schedule 1 poison list and should only be used under supervision of the certified doctor. Common adverse reaction from the use of azelaic acid includes skin irritation and redness.
Summary:
In Malaysia, the use of medicated pigment creams is very common. Because of its effectiveness, these ingredients often found its way into local skincare and cosmetic whitening products. Some of these locally made products were also found to have mercury, a poisonous compound that could cause potential deadly health problems. This poses a great risk to the consumers and expose its user to various potential adverse reaction. We have to be smart about what we put onto our skin. Never be afraid to ask your beautician or doctors about the ingredients used in their products. They should have complete insight about the ingredients of their products prior to selling them to you.
Our final advice to all our reader is, if you have pigmentation problems, consult your trusted certified dermatologist or medical aesthetic doctor before embarking on any treatment.
Reference:
- Bandyopadhyay D. TOPICAL TREATMENT OF MELASMA. Indian Journal of Dermatology. 2009;54(4):303-309. doi:10.4103/0019-5154.57602.
- Rashimi S, et. al.; Cosmeceuticals for Hyperpigmentation: What is Available? J Cutan Aesthet Surg. 2013 Jan-Mar; 6(1): 4-11. doi: 10.4103/0974-2077.110089
- Lauren Cooper, Aug 8, 2016, Avoiding Mercury Poisoning From Skin Care Products. accessed on 24/8/2018.
- World Health Organization & International Programme on Chemical Safety. (1994). Hydroquinone / published under the joint sponsorship of the United Nations Environment Programme, the International Labour Organisation, and the World Health Organization. Geneva : World Health Organization.
- World Health Organization, International Programme on Chemical Safety, United Nations Environment Programme & International Labour Organization. (1996). Hydroquinone : health and safety guide. Geneva : World Health Organization.
- Aersthetic Doctor Shares 5 Crucial Skincare Routine for Healtheier Skin, Dr Ko Skin Specialist. accessed on 24/8/2018
Disclosure of off labelled use:
This documents contains discussion of agents that are not indicated by the U.S. Food and Drug Administration. MalaysiaAesthetic.com, Allergan Inc, Merz Aesthetic and Ipsen Biopharm Limited, do not recommend the use of any agent outside of the labelled indication. The opinion expressed in this document are those of the contributors and do not necessarily represent the general concensus of The Medical Aesthetic Society, Allergan Inc, Ipsen Biopharm Limited and Merz Aesthetic. Please refer to the official prescribing information for each product for discussion of approved indications, contraindications and warnings.
Copyright, Legal Notice and Disclaimer:
The information presented in this document is not meant to serve as a guideline for patient mangement. This document is written based on personal experience and anecdotal evidence. The Author(s) and MalaysiaAesthetic.com assume no responsibility for errors or omissions in this text. Prior to deciding on any treatment, discuss with your certified doctor about the indication, potential risk and contraindication of the treatment. MalaysiaAesthetic.com shall not be liable to anyone for any loss or injury caused in whole or in part by your use of this information, or for any decision you make or action you take in reliance on the information you received from this writting.


With thanks! Valuable information!